What is the radiation footprint of radon on people on the Earth?

Radon is an environmental component and a naturally occurring source of ionizing radiation. Radon is responsible for around 50% of the earth’s natural radiation levels. It is created when uranium decays in soil, rocks, and water, after which it enters the atmosphere. Radon swiftly decays into radioactive particles, which are deposited on airborne particles, breathed, […]
What effect do natural radiation sources have on people on Earth?
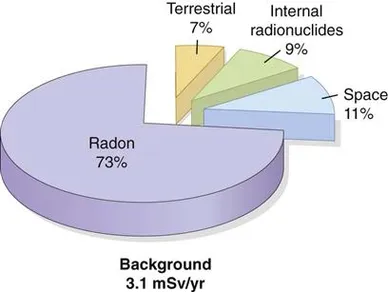
We receive: 73% (2.28 mSv) of natural radiation by breathing; 11% (0.33 mSv) reaches us via cosmic rays; 9% (0.29 mSv) through food and 7% (0.21 mSv) from other terrestrial sources.
What is the recommended indoor air humidity?
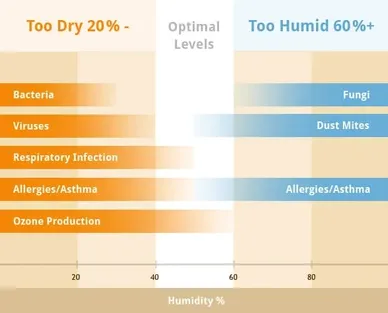
The recommended indoor air humidity is between 45% and 55%. Too low humidity is a prerequisite for the development of bacteria, viruses, respiratory infections, allergies and asthma. Excessively high humidity is a prerequisite for the development of spores, fungi, allergies and asthma.
What are the acceptable levels of radon in residential buildings?

The safe radon level in inhabited premises is up to 100 Bq/m3. If measurements of 100 to 150 Bq/m3 are taken over a period of more than three months, we highly recommend implementation of Radon mitigation measures. Radon levels more than 150 Bq/m3 measured over a period of more than one month necessitate prompt mitigating […]
What are the sources of radiation based on their wave frequency, and how do they impact the human body?
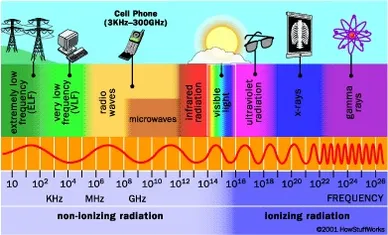
As the wave frequency rises, so does the energy with which it affects the human body. Following the visible spectrum, the waves are classed as ionizing radiation. Ionizing radiation harms the human body at the subcellular, cellular, and tissue levels, as well as the organism as a whole. The longer the radiation and the greater […]
Is it possible to do a radiation examination on a human being?
If a person has come into contact with or ingested radioactive materials that are still emitting alpha, beta, or gamma radiation, they may have radiation traces on them. A Geiger counter cannot identify ex-post exposure to radioactive material if the subject has been in contact with it but does not contain any active particles on […]